Lamp
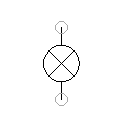
When current flows through the lamp, an optical signal is activated. In FluidSIM, the lamp is colored with the set color.
There are two different physical models to choose from.
In the case of a simple resistor, the lamp is modeled as an ohmic load with a constant resistance. The resistance is given by the nominal voltage and the nominal power.
If the temperature-dependent resistor
is chosen, the resistance increases as the temperature increases, as in a real light bulb. The relationship between cold resistance and hot resistance is observed here. The hot resistance is given by the nominal voltage and the nominal power.
Adjustable parameters
| Designation | Range | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| Physical model | Simple resistance, Temperature dependent resistance | Simple resistance |
| Rated voltage | 0.1 ... 400 V | 12 |
| Rated power | 0.1 ... 10000 W | 5 |
| Ratio R_cold:R_warm | 0.001 ... 1000 | 0.1 |
Failure models
| Failure model | Description |
|---|---|
| Filament blown | No current flows because the lamp has blown. |
| Short circuit | The lamp causes a short circuit. |
| Faulty voltage value | The nominal voltage specified in the failure configuration is used. This may lead to an unexpected flow of current. |
| Faulty power value | The nominal power specified in the failure configuration is used. This may lead to an unexpected flow of current. |
| Poor contact | An additional serial resistance specified in the failure configuration is used, in order to simulate an excessive resistance for example. |
| Designation | Range | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| Rated voltage | 0.1 ... 400 V | 30 |
| Rated power | 0.1 ... 10000 W | 1 |
| Resistance in series | 0.001 ... 1000 Ohm | 50 |